T2-preparation optimized for cardiac imaging
Value Proposition
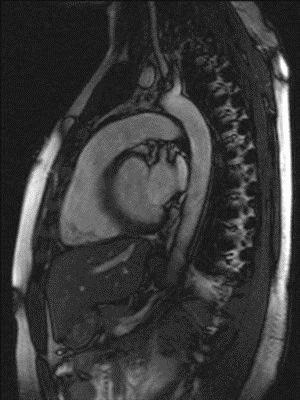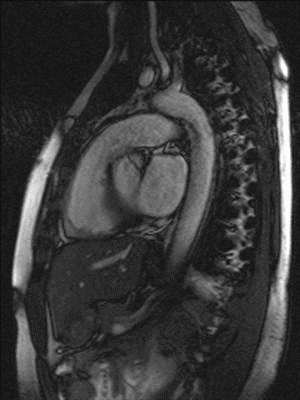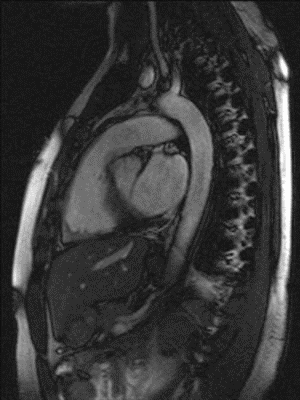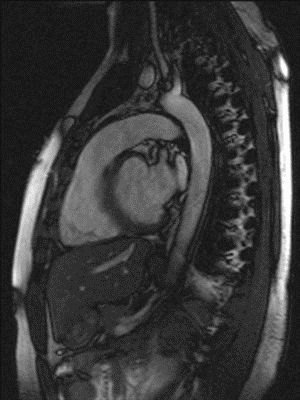
Myocardial infarction is the leading cause of death in the United States. T2-imaging of the heart is used to detect areas of myocardial edema which may aid in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Most existing T2-imaging methods are adversely affected by inhomogeneities of the magnetic excitation field B1 and/or the static magnetic field B0. Moreover, many existing methods are sensitive towards motion and flow, resulting in signal variations across the myocardium that can be mistaken for intensity changes due to pathophysiological changes. Thus, there is a need for a more robust T2-imaging modality that can overcome these limitations.
Technology
Researchers at Duke have developed a configurable T2-preparation technique for cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. The optimized adiabatic module achieved shorter inter-pulse spacing while exhibiting improved signal homogeneity. The method resulted in significantly higher image quality and higher insensitivity toward cardiac motion and flow. The new technique was tested in cardiac patients.
Other Applications
Can be used for any other organ to create T2-weighted magnetic resonance images
Advantages
- The method prepares the magnetization more homogenously than the standard T2 preparation
- Achieves excellent robustness sensitivity towards motion, flow, B1- and B0- inhomogeneity
- Effectively suppresses background tissue in coronary magnetic resonance angiography
- Highly useful in edema imaging