- Agriculture
- Antibiotic/anti-viral
- Biologics
- Biomarkers
-
By Clinical Application
×
- Anesthesiology
- Blood & Lymphatic Disease
- CNS & Neurosciences
- Dermatology
- Diabetes, Metabolism, Endocrinology & Obesity
- Ear, Nose, & Throat
- Emergency Services
- Gastroenterology & Digestive Disease
- General & Plastic Surgery
- Health Education, Medical Training and Operations
- Heart and Vascular
- Immunology, Autoimmune & Inflammation
- Infectious Diseases
- Mental Health
- Multiple clinical applications
- Musculoskeletal Disorders, Orthopedics/Bone
- Nephrology/Renal
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orphan Diseases
- Pediatrics
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Radiology
- Regenerative Medicine / Tissue Engineering
- Reproductive Health: Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Respiratory & Pulmonary
- Surgery
- Transplantation
- Urology
- Wound Healing
- COVID-19
- Creative Works
- Diagnostics
- Drug Delivery
- Drug screening and discovery
- Energy, Cleantech & Environmental
- Engineering & Physical Sciences
- Gene therapy
- Imaging
- Materials
- Medical Devices
- Nutraceuticals
- Other
- Research & Design Tools
- RNAi/siRNA
- Sensors & Controls
- Small molecules
- Software & Information Technology
- Stem Cells
- Vaccines
- Veterinary Medicine
A computer vision approach for molecular subtyping of breast cancer using MRI
Unmet Need Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in American women and the fourth most common cause of all cancer-related deaths in the U.S. While early screening for cancer using magnetic…
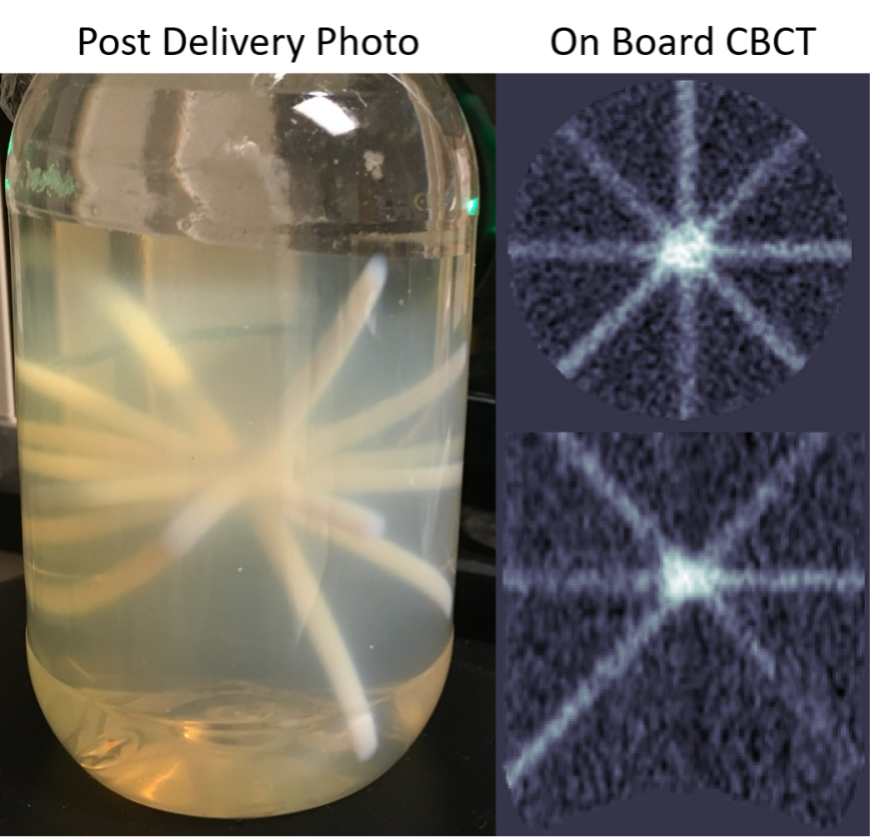
A method for end-to-end spatial accuracy quality assurance for radiosurgery
Unmet Need Radiation therapy is an essential element of cancer treatment that benefits 4 million diagnosed patients every year. The ability to deliver complex three-dimensional distributions of dose that conform to even irregularly shaped lesions…
Virtual frequency-selective inversion method for fat suppression in MRI
Unmet Need In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), data is acquired by a scanner that sends a sequence of radio frequency (RF) pulses into the tissue placed in a strong magnetic field. The magnetic field causes…
A method for validating complex radiation treatments using 3D dosimetry that can be implemented remotely
Unmet Need Radiation therapy is an essential element of cancer treatment that has been estimated to be potentially beneficial to 4 million diagnosed patients every year. The advent of commercially available magnetic resonance imaging guided…
Dynamic MRI of lungs using perfluorinated gas mixtures
Unmet Need Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the 3d leading cause of death in the US. It has consistently increased in frequency over the past 4 decades, currently including 15-20 million diagnosed cases. COPD…
A new method to improve contrast-enhanced MRI by suppressing blood pool signal
Unmet Need In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast agents are often used to enhance the difference between diseased and normal tissue. Images taken with contrast agents allow to identify myocardial infarction, stroke, tumors, atherosclerosis, tissue…
Software to determine lung function based on 19F MRI lung images
Duke inventors have developed a software to determine lung function based on 19F MRI lung images. This technology, called Washout, calculates quantitative functional values for anatomic regions of the lung by fitting a model to…
Single-cardiac-cycle phase sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) method for cardiac MRI
Unmet Need Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a safe, non-invasive test that creates detailed images of organs and tissues. In a typical MRI procedure, the subject is positioned in a strong magnetic field, and the…
MRI Imaging Sequence for Improved Contrast Using a Reference Image
Value Proposition Cardiac MRI is a useful tool in the diagnostic arsenal of clinical practitioners with an estimated 2 million procedures performed annually in the United States. The detail provided by this imaging modality is…
Magnetic resonance imaging method for detecting magnetic field oscillations
This invention is a new magnetic resonance imaging method that can detect magnetic field oscillations in specific frequency bands, in particular those induced by neuroelectric activity in the brain. In contrast to existing neuroimaging techniques,…