A system and method for planning radiosurgery treatments that can better target multiple tumors simultaneously
Unmet Need
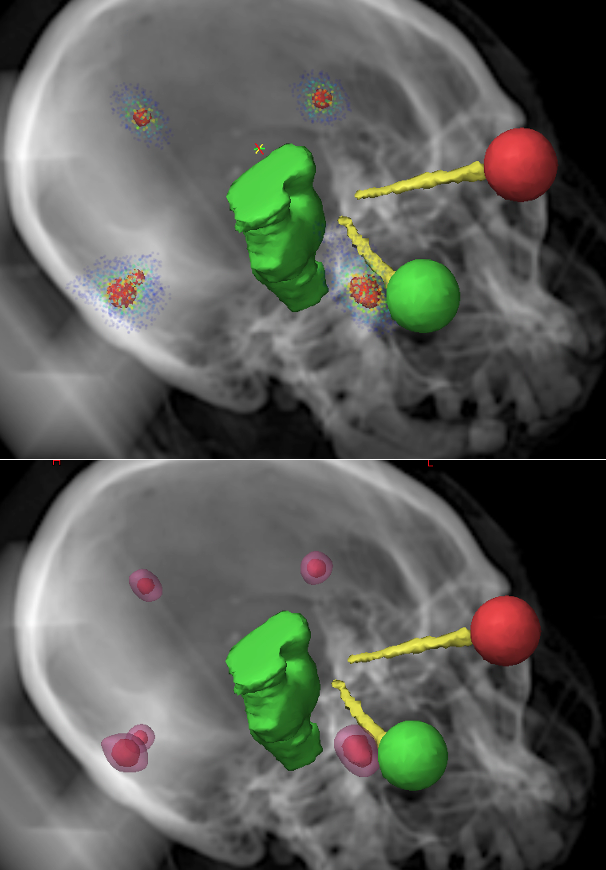
Brain metastases are the most common neurological complication of primary cancer and are estimated to occur in 9-17% of all cancer patients. Radiosurgery has become a standard treatment technique for brain metastases, which now includes the ability to treat multiple metastatic brain lesions simultaneously. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is commonly used to plan linac-based radiosurgeries, but it can lead to increasingly complicated treatment plans and unnecessary radiation of healthy tissue as the number of targets increases. There is a need for technologies that improve the treatment of multiple tumors with radiation therapy.
Technology
Duke inventors have developed a system and method for planning radiosurgery treatments intended to reduce the radiation received by healthy tissue when treating multiple tumors, especially during brain metastases treatments. Specifically, the method, termed Conformal Arc Informed Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (CAVMAT), provides a simple, intuitive starting point at which the radiotherapy treatment plan can be optimized. In treatment planning studies the technology provides exceptional target coverage and normal tissue sparing while minimizing plan complexity. Importantly, the relatively less complex treatment plans were shown to be more robust to uncertainties in the dose calculation algorithm and beam modeling than were the standard treatment plans.
Advantages
- Can reduce radiation received by healthy tissue for treating multiple tumors
- Results in less complex treatment plans that are more robust to uncertainties in beam modeling
- Planning process that can be easily automated, decreasing the workload for treatment planners